Why Enterprise Application Testing is Crucial for Business Success
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, staying ahead of the competition is more challenging than ever. As the owner of Quality Professionals, a business dedicated to providing top-notch enterprise solutions, you understand the importance of delivering seamless and reliable software applications to your clients. But have you ever considered why enterprise application testing is crucial for your business’s success? In this article, we will delve into the world of enterprise application testing and explore how it can make a significant difference in achieving your business goals.
Understanding Enterprise Application Testing
What is Enterprise Application Testing?
Enterprise Application Testing, often referred to as EAT, is a critical phase in the software development lifecycle. It encompasses a series of processes and methodologies aimed at evaluating and validating complex software applications that cater to the specific needs of large organizations. These applications, commonly known as enterprise software, are the digital backbone of businesses, facilitating various essential functions, including data management, process automation, and communication within the organization.
The Essence of EAT
The essence of Enterprise Application Testing lies in its mission to ensure that these software applications function flawlessly and consistently under diverse conditions. It involves subjecting the software to rigorous assessments to detect and rectify any issues, thereby guaranteeing that it meets the highest standards of quality, reliability, and security. This meticulous approach helps organizations avoid the potentially catastrophic consequences of software failures, which can include financial losses, damage to reputation, and compromised data security.
The Scope of Enterprise Application Testing
Enterprise Application Testing is a comprehensive process that covers various dimensions of software quality, including:
- Functional Testing: This aspect focuses on assessing whether the software’s functions and features perform as intended. Testers verify that the application meets the specific business requirements and objectives.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating how the software performs under different conditions is crucial. This includes assessing its speed, responsiveness, and scalability to handle increasing workloads.
- Security Testing: With the increasing threat of cyberattacks, security testing is paramount. It identifies vulnerabilities and ensures that sensitive data remains protected.
- Usability Testing: Ensuring that the software is user-friendly is vital for enhancing user adoption and satisfaction. Usability testing evaluates the application’s interface and overall user experience.
- Compatibility Testing: As enterprise applications need to work across various platforms and devices, compatibility testing ensures that the software functions correctly on different configurations.
- Regression Testing: This ongoing testing process ensures that new changes or updates do not introduce defects into previously working parts of the software.
The Benefits of EAT
Implementing Enterprise Application Testing offers numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Enhanced Reliability: By identifying and fixing issues before deployment, businesses can rely on software applications to perform consistently.
- Cost Savings: Early detection of software defects minimizes the costs associated with fixing issues post-launch.
- Improved Security: Security testing helps protect sensitive data and safeguards against potential breaches.
- Enhanced User Experience: Usability testing ensures that end-users can efficiently interact with the software, leading to higher user satisfaction.
- Competitive Edge: Delivering high-quality software can set a business apart from its competitors and build trust with clients.
The Significance of Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) is a systematic and vital process in the field of product and service development across various industries. It is a comprehensive approach that ensures that products, services, or processes meet predefined quality standards and consistently deliver a high level of performance and reliability. The significance of QA extends far beyond just checking for defects; it encompasses a range of critical functions and benefits.
Ensuring Product Quality
At its core, QA is about ensuring the quality and integrity of products or services. By implementing robust QA processes, organizations can:
- Minimize Defects: QA identifies and rectifies defects early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of issues reaching customers.
- Consistency: QA ensures that products or services are consistent in quality, meeting or exceeding customer expectations every time.
- Compliance: It ensures that products or services adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards, preventing legal and compliance-related issues.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
One of the primary goals of QA is to enhance customer satisfaction. When customers receive products or services that consistently meet their expectations, they are more likely to become loyal and repeat customers. This can lead to increased customer retention and positive word-of-mouth referrals, which are invaluable for businesses.
Reducing Costs
QA may require an initial investment in terms of resources and technology, but it often leads to cost savings in the long run. By identifying and resolving issues early, organizations can avoid expensive recalls, rework, or customer complaints. Additionally, QA helps optimize processes, reducing waste and inefficiencies.
Mitigating Risks
QA plays a crucial role in risk management. It helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in products, services, or processes and allows organizations to proactively address them. This minimizes the likelihood of unexpected failures or crises, protecting the organization’s reputation and financial stability.
Supporting Continuous Improvement
QA is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment to quality. It encourages organizations to continuously monitor and improve their processes, products, or services. Through feedback mechanisms and data analysis, QA provides valuable insights that drive innovation and optimization.
Industry-Specific Significance
The significance of QA is not limited to a specific industry; it is relevant across various sectors, including:
- Manufacturing: QA ensures that products meet safety and quality standards, reducing defects and recalls.
- Healthcare: QA in healthcare helps improve patient safety, compliance with regulations, and the overall quality of care.
- Software Development: In software development, QA ensures that applications are free of bugs, perform well, and are secure.
- Construction: QA in construction ensures that buildings and infrastructure projects are safe, durable, and meet design specifications.
- Food Industry: QA is critical in food production to guarantee the safety and quality of food products.
Benefits of Enterprise Application Testing
Enhanced Performance
One of the primary advantages of rigorous testing is improved performance. Enterprise applications need to handle a vast amount of data and users simultaneously. Testing identifies and resolves performance bottlenecks, ensuring smooth operations even during peak usage.
Error Reduction
Errors in enterprise applications can lead to costly downtime and security breaches. Thorough testing helps identify and rectify these errors before they can impact your client’s operations. This proactive approach minimizes business disruption and potential financial losses.
Security Assurance
Data breaches can have devastating consequences for a business’s reputation and finances. Robust security testing is essential to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that sensitive information remains protected.
The SEO Connection
SEO and Enterprise Application Testing
As a seasoned SEO specialist, you already know the importance of website performance in search engine rankings. Enterprise applications play a significant role in enhancing user experience, which, in turn, can boost your client’s website’s SEO performance. When applications are responsive, fast, and error-free, users are more likely to engage with the site, leading to improved search engine visibility.
Implementing Enterprise Application Testing
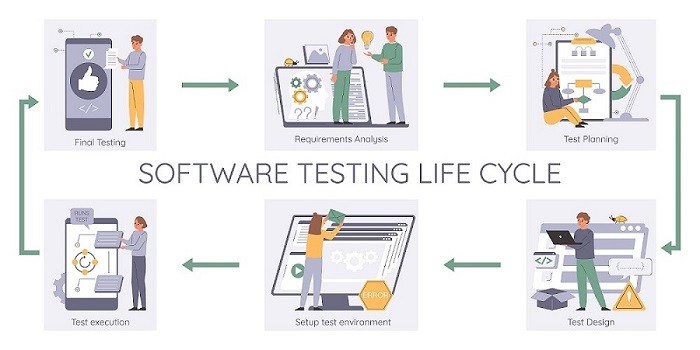
Implementing Enterprise Application Testing is a structured and systematic process that involves a series of essential steps and considerations. These steps are crucial for ensuring the successful evaluation, validation, and optimization of complex software applications tailored for large organizations.
1. Requirement Analysis
The first step in implementing Enterprise Application Testing is understanding the specific requirements and objectives of the project. This phase involves close collaboration with stakeholders, including clients, project managers, and end-users. Key activities in this phase include:
- Gathering Requirements: Collecting detailed information about the application’s intended functionality, performance expectations, security requirements, and user experience goals.
- Defining Test Objectives: Establishing clear testing objectives that align with the project’s overall goals and client expectations.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks and challenges that may impact the testing process or the application’s performance.
2. Test Planning
Once the requirements are well-understood, the next step is to create a comprehensive testing plan. This plan serves as a roadmap for the entire testing process and includes the following components:
- Scope: Clearly defining the scope of testing, including which parts of the application will be tested, which types of testing will be performed, and any testing limitations.
- Test Strategy: Outlining the overall testing approach, methodologies, and techniques that will be used.
- Resource Allocation: Determining the human and technological resources required for testing, including testing environments and tools.
- Test Schedule: Establishing timelines for each testing phase, including start and end dates for test execution and reporting.
3. Test Execution
The test execution phase is where the actual testing of the application takes place. Depending on the project’s complexity, this phase may include various types of testing, such as:
- Functional Testing: Evaluating the application’s functionality to ensure it meets the specified requirements.
- Performance Testing: Assessing the application’s speed, scalability, and responsiveness under different conditions.
- Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring data protection measures are in place.
- Usability Testing: Testing the application’s user interface and overall user experience.
During this phase, testers meticulously follow predefined test cases and scenarios, documenting any issues or defects they encounter. They also monitor the application’s performance and record relevant metrics.
4. Bug Tracking
As issues and defects are identified during testing, they are documented in a bug tracking system. Each issue is categorized based on its impact and severity, allowing project managers and developers to prioritize and address them accordingly. Effective bug tracking ensures that no critical issues are overlooked and that all defects are resolved before the application’s release.
5. Reporting
Once the testing phase is complete, detailed reports are generated to summarize the testing results. These reports include:
- Test Summary: An overview of the testing process, including the scope, objectives, and methodologies used.
- Test Results: A detailed account of the testing outcomes, including any defects discovered and their status.
- Recommendations: Suggestions for addressing the identified issues and improving the application’s quality.
- Conclusion: An overall assessment of the application’s readiness for deployment.
6. Iterative Testing
In some cases, iterative testing may be necessary. This involves revisiting certain testing phases to ensure that issues have been adequately addressed and that the application meets the required quality standards. Iterative testing continues until all stakeholders are satisfied with the application’s performance and quality.
Conclusion
In the competitive business landscape, delivering reliable and high-performing enterprise applications is non-negotiable. Quality Professionals understands that enterprise application testing is the linchpin of success in this arena. By investing in rigorous testing processes, you can ensure that your clients receive top-tier software solutions that drive their business forward.

FAQs
- Why is enterprise application testing essential for business success? Enterprise application testing ensures that software applications perform optimally, reducing errors, enhancing security, and boosting performance.
- How does enterprise application testing impact SEO? Seamless and error-free applications contribute to better user experiences, which can positively affect a website’s SEO rankings.
- What are the key steps in implementing enterprise application testing? The process includes requirement analysis, test planning, test execution, bug tracking, and reporting.
- Can Quality Professionals assist with enterprise application testing? Yes, we specialize in delivering comprehensive testing solutions tailored to your business’s needs.
- Where can I learn more about enterprise application testing? Access more information and resources at Quality Professionals.
Remember, enterprise application testing is not just about meeting industry standards; it’s about exceeding client expectations and driving their business towards unparalleled success.

