Guidelines On How To Test Blockchain Implementation
The Blockchain Implementation world should be familiar to everyone who works with digital currencies. After conducting thorough research, we have concluded that blockchain technologies may be leveraged to transform your company. Follow these guidelines on how to test blockchain implementation.
The Following are the steps involved in Testing Blockchain Implementation:
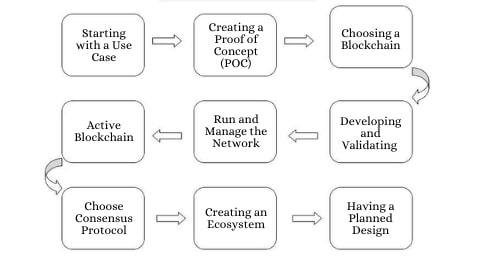
1. Starting with a Use Case
To begin, this is the most crucial step in the blockchain implementation process. To identify a use case, you must first research, explain, and organize your blockchain requirements. Next, you must choose relevant blockchain use cases to examine, research, and explore extensively before incorporating them into your blockchain implementation.
2. The Importance of Creating a Proof of Concept (POC)
The next stage is to construct a valid Proof of Concept (POC) for your use case. POC is a strategic approach for determining whether or not a blockchain implementation is feasible for your company. It’s critical to emphasize that “direction” is essential to developing your Proof of Concept. You should be able to see what your actions might lead to. In a nutshell, you should be tactical and deliberate in your actions and conclusions.
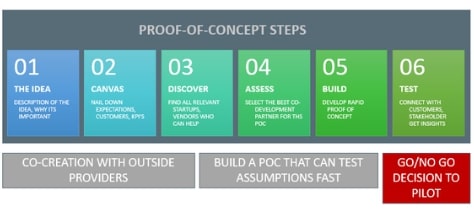
The steps for creating a Proof of Concept are as follows:
- Create and adhere to a set of standards that describe the scope of your company’s endeavor.
- Make a prototype that includes sketching, design, coding, architecture, and other elements.
- Put your prototype to the test.
- Analyze your MVP with the bare minimum of desired top characteristics. The term “minimum viable product” refers to a product that meets the basic minimum requirements.
3. Carefully choosing a blockchain

When choosing a blockchain platform for your company, it’s critical to be deliberate and cautious. This is a strategic step in which you must think about your budget and do extensive research. There are several well-known platforms to choose from when choosing a Blockchain for your organization.
Some of the most well-known blockchain platforms are:

- Ethereum: It is primarily used to create creative contracts. Many companies are already using it to estimate their business’s prospective growth rate.
- Quorum: Many businesses have used Quorum as part of their blockchain implementation. Quorum essentially eliminates data tampering in commercial transactions.
- Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain technology that allows corporations and organizations to construct private, public, chain-based applications.
- Stellar: It is a blockchain platform used to create blockchain applications for businesses and organizations.
- Corda: A blockchain platform expert would produce unique designs while also exploiting the platform to eliminate all costly contingencies in your business contracts. It enables you to conduct direct transactions using smart contracts that ensure the highest security and anonymity.
- Open the chain: The main goal of this blockchain platform is to take advantage of blockchain technology to improve every element of your company’s human resource management.
- Multichain: The Multichain platform may be used in various industries, including banking and finance, healthcare, human resources, e-commerce, education, retail, and so on. It is mainly utilized for professional human resource optimization in your company.
4. Developing and Validating a Blockchain Solutions
It’s a good idea to keep up with the latest blockchain technology so you can pick the ideal one for your needs. This procedure entails assessing several variables, including:
- Blockchain technology’s infrastructure.
- It’s also important to know whether it works with both private and public blockchains.
- Is it compatible with multichain and other various platforms because of the breadth of the technology?
The functionality of smart contracts is one of the essential aspects of blockchain technology. Smart contracts allow firms to conduct critical transactions without third parties, and this has the advantage of making the transaction process more automated, transparent, and fair. Testing your system requires testing apps on several platforms.
5. In production, run and manage the network

To accomplish this, you must first construct your block. Keep in mind that this block must have all of the chain’s attributes. Essentially, this step lays the groundwork for receiving data. At this point, the encrypted token, more commonly known as cryptocurrency, enters the picture. The encrypted token would activate the power required to ensure that the nodes’ communication would stay persistent.
6. Active Blockchain
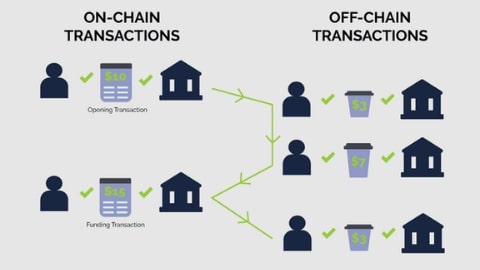
All that remains is to activate an application on the blockchain network after the network has been set up and managed. This is an application server that is ready to use. Each of your applications would be hosted on the main blockchain in this case. It is advised that you initialize hybrid solutions on the cloud server if we are on-chain and off-chain entities.
7. Choosing the Most Appropriate Consensus Protocol
The goal of Proof of Work is to protect against cyber-attacks like DDoS or Distributed Denial-of-Service attacks. The agreement in this consensus system is based on the amount of cryptocurrency held by miners or the ‘weight’ of their coins.
In most Proof of Stake implementations, the miner must validate block transactions based on the number of coins they own. This consensus protocol ensures that transactions are approved. A miner’s ability to create more blocks is proportional to the amount of cryptocurrency in their possession.
8. Creating an Ecosystem
When a large number of stakeholders become involved in the blockchain, an ecosystem becomes necessary. An ecosystem will function as a subset of the greater blockchain community. It will serve to boost understanding of the sector and encourage business trust. Stakeholders must agree on the following issues in order to create an ecosystem:
- The terms of the contract
- How to ensure that costs and benefits are distributed fairly.
- The governance procedures that have been put in place.
- Having a Planned Design
9. Having a Planned Design
Every blockchain specialist will agree that the blockchain’s structure necessitates careful planning. The design must be purposeful to ensure that any faults with the organization are quickly resolved.


